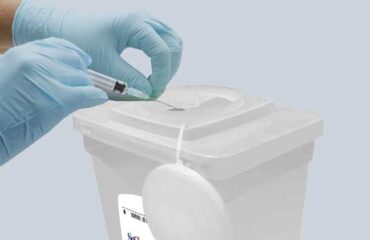
Understanding Biomedical Waste
Biomedical waste, often referred to as medical waste, encompasses a wide range of materials generated during healthcare processes. This waste includes used needles, syringes, blood-soaked dressings, expired medications, contaminated laboratory materials, and more. It can pose significant risks to human health and the environment if not managed properly.
Health Risks
Improper disposal of biomedical waste can expose healthcare workers, patients, and the general public to serious health risks. Contaminated materials may carry infectious agents, pathogens, and harmful chemicals. Accidental contact with such waste can lead to the transmission of diseases, posing a grave threat to human safety.
Environmental Hazards
Biomedical waste not only endangers human health but can also harm the environment. The disposal of hazardous chemicals and pharmaceuticals into landfills or improper incineration can contaminate soil and water sources. This pollution can have long-lasting consequences, affecting ecosystems and, indirectly, human well-being.
The Crucial Role of Biomedical Waste Management
Effective biomedical waste management plays a pivotal role in mitigating these risks. It involves a systematic approach to collecting, segregating, transporting, treating, and disposing of waste materials generated in healthcare facilities. Here’s how it contributes to enhancing human safety:
1. Protecting Healthcare Workers
By implementing proper waste management protocols, healthcare workers are shielded from accidental exposure to hazardous materials. Sharps containers, for instance, are designed to safely collect needles and sharp objects, reducing the risk of needlestick injuries.
2. Preventing Infection Spread
Biomedical waste management ensures the safe disposal of infectious materials, preventing the spread of diseases within healthcare settings. This protects both patients and staff.
3. Environmental Protection
Sound biomedical waste management safeguards the environment by preventing the contamination of air, soil, and water. This, in turn, protects the broader community from exposure to harmful substances.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare facilities must adhere to strict regulations and guidelines regarding biomedical waste management. Compliance ensures that safety standards are met and that legal requirements are fulfilled.
Sustainable Biomedical Waste Management
In recent years, the focus has shifted towards sustainable biomedical waste management practices. Healthcare facilities are exploring ways to minimize waste generation, reduce the use of disposable items, and implement eco-friendly disposal methods. By doing so, they not only enhance safety but also contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Biomedical waste management may operate in the background, but its impact on human safety and environmental well-being is undeniable. By properly managing and disposing of medical waste, healthcare facilities demonstrate their commitment to the health and safety of their patients and staff, as well as their responsibility to protect the planet. As healthcare continues to evolve, it is crucial to prioritize and invest in effective biomedical waste management for a safer and more sustainable future for all.
 Get Quote
Get Quote